Big Data Guide – Explaining all Aspects 2024 (Update)
-
 By Nandini
By Nandini - Published on Dec 12 2022

Table of Contents
Introduction
A Comprehensive Guide to Big Data
Look around you, and there won’t be a single object that doesn’t depend on technology. From smartphones to smart TVs, we have incorporated technology seamlessly into our lives. This technology is not a singular entity. It is a combination of software, hardware, and a lot of intermediate things.
The majority of these ordinary things can be termed "data." Data science is one of the most popular streams being followed by people all over the world. Data science is the collection and analysis of data to obtain information from it.
Now, the question that arises is,
What is Data? How do we Define Data?
In simple words, "data" can be defined as the inputs given by hardware that get stored in the software. We use equipment like our keyboards, smartphones, or microphones to input or upload data that gets stored on servers.
Anything that gets stored in a computer in the form of electrical inputs can be termed "data." The transmission of data occurs through electrical, magnetic, or mechanical waves.
Now that you have understood what data is, let’s go to the next thing about data science, which is big data.
What is Big Data?
With the vast rise of IT in every sphere of our lives, there is an enormous amount of data generated daily. This data can be termed "big data." So, is any data present in huge size known as "big data"? Well, in a way, yes.
Big Data is Data multiplied over a thousand billion times. The definition of Big Data is a humongous amount of data stored in a system that is continuously growing in size. This growth in size is not linear but exponential.
The exponential increase in size can be attributed to the rise in the number of things being added to the global pool of networking every day.
A steady rise in the human population can also contribute to this big data. You might ask what constitutes big data, and why is it so significant? When we talk about the size of big data, we’re not talking in bytes, megabytes, or gigabytes. Here, we are talking about petabytes.
A petabyte is equivalent to 1,048,576 gigabytes of data! This amount is the data generated in a single day per service. To give you a rough estimate of the enormity of a petabyte, it would take nearly 70,000 computers to make one petabyte of data.
This is how sizeable Big Data is. The magnitude of a petabyte is such that we still don’t have a storage option for a single petabyte. Maybe, in the next decade, we will develop a unique system to store petabytes, but that future of Big Data is still some years away.
Criteria for Big Data
Precisely what can be considered "big data" can be identified with simple concepts. The nature of data is analyzed, and there are specific criteria that, if fulfilled, will classify data as big data. Let’s look at the requirements for data to be termed "big data."
- Amount of data stored: The volume of data stored in big data databases is enormous. And the data keeps growing exponentially. So any broad data, almost the capacity of petabytes, would be considered big data.
- Sources of generation: Some sources, like social media and data centers, generate enormous amounts of data. The variety of data being generated is also essential, as it will allow you to understand the nature and characteristics of the data.
- Speed of extraction: The rate of retrieval of data or the velocity of Data is also responsible for categorizing data as "big data." Processing the raw data into something that can be interpreted is a big part of big data analytics.Sieving through the data and finding the ones that are useful are also important.
- How data is organized: With such vast amounts of data involved, it is easy to lose track of what you are storing. Segregating data into places where they can be obtained easily is equally important. The quality of the data also needs to be taken into consideration. It is pointless if you create large databases to store data but the quality is not up to par.
Big Data Concepts and Big Data Examples
Big Data concepts have always relied on giving real-life examples to explain the concept of big data. To help you estimate how much data is generated per day by big data companies, here are some mind-boggling big data examples:
- The most prominent example of a big data ecosystem is social media, which is the most significant contributor to big data. Every day, social media generates massive amounts of data. These data are in the form of messages, comments, likes, shares, uploaded photos, videos, or social media activity.
The largest social media platform, Facebook, generates nearly 550 terabytes of data in a single day! If you’re not aware of how significant one terabyte is, it is 1024 Gigabytes.
Imagine an average of 550 terabytes being stored per day. That Data gets doubled every two days. When you consider the additional number of people joining Facebook, the number keeps growing exponentially.
- Another example of big data is the data obtained from airplanes. The engine of a regular aircraft can contribute as much as 15 terabytes of data in 30 minutes. This amount can vary depending on the type of aircraft.
Het engines generate much more data, and so do cargo planes. An airport or airline service has to operate thousands of flights per day. When you consider the amount of data for a 30-minute flight, the total data generated per day can go up to several petabytes.
- Banks are a classic example of big data. Even in the earlier days, banks used to generate large amounts of data. The infrastructure back then was not capable enough to store such enormous quantities of data.
A lack of adequate storage leads to the mismanagement of data that is usually lost among thousands of other data items. With the development of newer technologies, it has become easier to sort through data and store it conveniently.
- Stock exchange corporations also generate extensive data per day. The biggest generator of big data among stock exchanges is the NYSE or the New York Stock Exchange. According to an estimate, the NYSE contributes one terabyte of data every day.
Big data frameworks come to the aid of these stock exchanges and allow them to store the enormous data. Big data companies stock the data in such a way that they can access it whenever they want.
By now, you are aware of the size of big data. Here, it is imperative to understand that traditional storage systems are not enough to handle all these data. An average hard drive can store a few gigabytes of data.
To save a petabyte of data, you would need nearly 480 large data centers, with the size of each data center being equal to 2000 football fields. And, if this is not shocking enough, the total estimated cost to store one petabyte of data in a single storage device is nearly $94,000,000,000,000. Phew! That’s a significant number.
This large amount of Data needs a system of large storage units. Big data technologies make it possible for us to store such vast amounts of data. These technologies combine the resources available to us with the current IT infrastructure available to deliver a system that can store petabytes of data.
Significant data architecture is spread over vast areas, sometimes covering areas that are the size of an average country. Significant data challenges are enormous.
These challenges are ever-growing because big Data is still in its initial stages. We have a lot to understand about it.
That was all you needed to get warmed up to big data. Now, let’s understand the different types of big data.
What are the Types of Big Data?
Prominent data characteristics allow us to classify it into three broad concepts or types. These types are structured, unstructured, and semi-structured. The classification is based on the nature of the data stored. Here is a detailed analysis of all the types of big data that you must know.

1) Structured Big Data
Structured big data is any data of enormous size that can be sorted into a definitive format. This could include a lot of real-life examples. The data sheet prepared by shopping companies to store the details of customers is an example of structured data.
In simple words, structured data is presented in a coherent form that is easy to understand. Structured data usually follows a linear structure and is organized based on specific characteristics. This is the best kind of data to work with, as it would pose no problem for you to obtain it, analyze it, process it, and gain useful information from it.
The most significant advantage of structured data is that it will help you predict issues that might arise during storage. Structured data is also known as comparable data because it is consistent throughout.
Large amounts of data are being stored over the internet with each passing minute. Getting a hold of them is next to impossible. In this case, structured data comes to our aid.
Structured data can be in petabytes or even zeta bytes. One zettabyte is equivalent to 1 billion terabytes. Some companies that have an extensive network of employees, clients, stakeholders, and customers rely on significant data benefits to store and access their data.
2) Unstructured Big Data
Unstructured data can be defined as any data that doesn’t have a definite form or path of flow. Unstructured data is hard to process because it is scattered and has no sequence.
In structured data, there is usually one characteristic that is used to classify and sort the data into different forms. But, with unstructured data, the case is entirely different. This unstructured data is considered "raw data."
Information is hard to process because nobody has any tools to start with it. There are large companies that generate petabytes of data each day, but due to a lack of tools and the availability of the data in an unstructured format, it becomes difficult to obtain any valuable information from it.
Unstructured big data can also be termed "heterogeneous" data because there is no consistency in it. The best example of unstructured big data is a search engine. Search engines store humongous amounts of data generated by users. This data is accessible to us, but it is still in an unstructured format.
The billions of pictures, videos, books, and other information we obtain from the internet consist of unstructured data. Unstructured big data usually has a combination of different types of data that are hard to process.
3) Semi-structured Data
Semi-structured big data is a mix of both structured and unstructured big data. Semi-structured data is usually represented in the form of HTML or XML files. Semi-structured data can be anything, ranging from the data collected by websites to your search history.
The cookies that sites usually collect to process and analyze their internet traffic and understand your search patterns also form semi-structured big data.
Transactions carried out all over the world also contribute to the growing mass of semi-structured data. This semi-structured data is one of the most significant contributors to big data.
Benefits of Big Data Analysis
There are several benefits to big data analysis. The main advantage of analyzing big data is that the information would be readily available to you. Sorting through large amounts of data to find something useful is the main motive behind big data analysis.
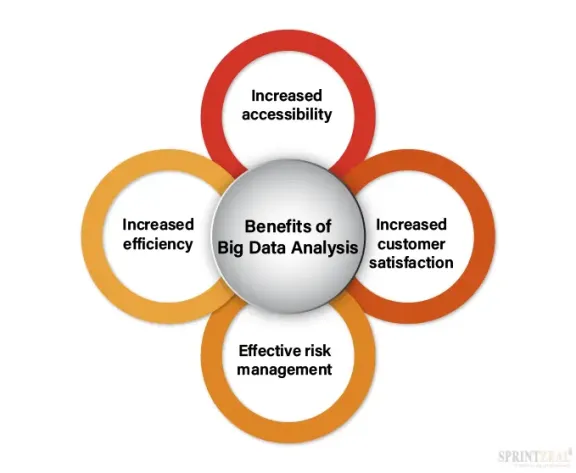
If you want to reap the benefits of big data and are wondering how it helps in the first place, here are some things that you need to consider.
1) Increased accessibility.
Accessibility is the most significant advantage of big data analysis. Once you store your data in efficient processors or servers, you would be able to obtain any information you want at any time.
Considering the bulk of data generated over the years, some of them might become obsolete after a few years. Big data analytics tools have been designed, keeping in mind the growing needs of the economy.
Social media sites are the best examples of how they have made big data accessible. You could browse through your profiles and search for any information, even if it was posted a decade ago.
The increased accessibility has made data storage and retrieval convenient for many people. It has also spurred the development of cloud services.
2) It has increased customer satisfaction.
Customers play an important role in deciding the future of any organization. This is the reason why a large number of companies are paying more attention to the needs and requirements of their customers.
Getting feedback from customers is an inseparable part of any business. But to get feedback from customers and then use it effectively, it requires special techniques and tools.
Big data analysis tools are meant for this specific purpose. They help companies obtain customer feedback and then store it in large databases.
The organizations can then choose to receive any information that they think might be beneficial to their growth. Prioritizing the data and then choosing to focus on only the relevant ones is the key to effectively using big data analysis.
3) Identification of risks and effective risk management
Risks are an inherent part of every business process. No company or project is risk-free. This risk can significantly impair the profitability of the organization because it results in huge losses every year.
Identifying risks becomes easier with big data analysis because you can predict the pattern of growth through the humongous amounts of data generated and stored. There are powerful analytical tools that will help you sort through significant amounts of data and establish a familiar dialogue between them.
Once you have identified the risk factors, it becomes easier for you to keep track of your company’s progress. Risk management has been made easier with the help of big data analytical tools.
4) Increased efficiency.
Customers depend on your organization for two things. One is the quality of services, and the other is efficiency. Both of these factors play a significant role in determining how far you will go as a company. The big data analytics tools will help you to become more efficient by allowing you to improve the speeds of data extraction.
When a customer would approach you with a query or a request, you would be able to address their issues quickly because of the efficiency of the data extraction process.
Imagine this. Someone has a complaint with one of your products and asks to know about the details of the product. For a company like Walmart that has millions of products, finding the details of just one would be next to impossible.
In this case, big data analytical tools help you find out the required data in a short period of time. As a result, your work processes become more efficient.
Big Data Analytical Tools
After knowing the benefits of big data analytics tools, you might be interested in finding out what tools are currently being used by people across the world. Here are some of the best and the most efficient big data analytical tools that are used.

1) Microsoft Power BI
Microsoft Power BI has been the favorite tool of many big data analysts. It is preferred for its ease of accessibility.
2) Oracle Analytics Cloud
It works on a consumption-based usage model and is known for its capacity to combine robust infrastructure with powerful techniques.
3) Splunk
Splunk has found popularity among organizations that were struggling with web-based log inspection. It uses powerful analytical tools and security control mechanisms.
4) Tableau
The name "Tableau" suggests that it uses tables and graphs to get the job done. This is somewhat true, as Tableau uses visualization of the data to incorporate big data analysis into the data extraction and analysis processes of large corporations.
5) Pentaho Big Data Integration and Analytics
Pentaho combines automation with data science. It uses open-source networks to process the different types of data available.
Careers in Big Data
After the above discussions, you must be confident that big data is a non-negotiable part of business giants. Forget about giants; even small-scale businesses are depending on big data for their business processes.
The career scope in this sector is enormous, and with the right preparations, you would immensely benefit from it. Big data has been proved to affect businesses in a transformative way. The affiliation of companies towards big data means that the job opportunities in this sector are bound to grow.
It is tough to become a prominent data specialist. The job of a significant data professional is demanding and would require every ounce of energy that you have.
Salaries for leading data professionals are lucrative, and when you consider that, the hard work doesn’t matter much. But before we tell you about the career paths in Big data, you need to understand the concept of Hadoop in big data.
Popular Job Titles in data science & business intelligence by National Avg. Salary(in dollars)
What is Hadoop?
A Hadoop architect specializes in semi-structured data like text, videos, audios, logs, etc. If you work as a Hadoop architect, you have to create designs to store enormous amounts of data, also known as big data.
The original programming language used by big data Hadoop architects was Java, but now, flexible languages like Python and R are being used. Rather than storing data in a single system, Hadoop stores it across multiple networks and channels.
This increases the disk transfer speed and allows a company to improve its networking and data extraction velocities.
The Hadoop architect in big Data is in high demand these days as companies desperately need skilled professionals who will be able to help them build robust significant data infrastructure. The average annual salary of a Big-data Hadoop professional is around $200,000.
Here are the learning paths that you can follow to become a big data professional.
1) Big Data and Hadoop Certification Course
Big Data Hadoop certification allows you to cover all the concepts of Hadoop 2.7. You get complete training on the different Big Data and Hadoop concepts. It is perfect for software developers, data management professionals, project managers, data scientists, and anyone who wants to make a career in big data and Hadoop.
Get Big Data Hadoop Analyst Certification Training
2) The Apache Spark and Scala Certification Course
Apache Spark is an IT framework that enables a learner to be proficient in data transformation and data mapping techniques. After completing this course, you will be able to use programming languages to create systems for storing big data and also devising network plans to maintain them.
After completing the Apache Spark and Scala certification courses, you have two options:
MongoDB-
This can be taken after completing the Apache Spark and Scala certification courses. It specializes in high-level programming languages like Java and Node JS. The MongoDB certification will enable you to store vast amounts of unstructured data in a MongoDB environment.
Cassandra-
The Apache Cassandra database specializes in database management and helps you store petabytes of data. You will be able to manage multiple data centers without any fuss. It has been designed for those IT professionals who wish to become Data scientists.
3) The Apache Storm Certification Course
To become a big data professional, you would need to complete this certification course. It will give you an understanding of how big data processing is used for real-time events. The course provides expert-level knowledge on JavaScript.
4) Apache Kafka Certification Course
This certification will make you the most sought-after employee in the IT industry. This allows you to integrate real-time messaging with data centers and use your knowledge of data management to process and analyze billions of messages in a short time.
Kafka has become synonymous with Big Data processing, so it is a must-have certification for you.
5) The Impala Certification Course
The Impala is the last and probably the hardest learning path to become a significant data architect. This course is designed to impart basic knowledge of SQL and Massively Parallel Processing (MPP). It is a query engine that is integrated with the Big data system. It eliminates the time-consuming process of data loading and gives immediate results. The role of Impala in Big data ecosystems is recognized by employers, so they look for candidates who have specialized in the Apache Impala certification course.
Explore some popular Big Data course options like,
Big Data Hadoop and Spark Developer Course
Careers and Job positions in Big Data
A career in Big Data is one of the most sought after positions in the IT industry. Here are some of the job positions that you can opt for as a big data professional.
1) Big Data Engineer
Big data engineers are in high demand in the IT industry as they help organizations process a large amount of data into coherent information. The salary of a big data engineer is nearly $130,000 annually.
2) Big Data architect
A big data architect has to design the framework of big data databases and has to oversee its upkeep. The annual salary of a big data architect is around $120,000.
3) Big data analyst
The role of a big data analyst is somewhat similar to data engineers. They help organizations make better decisions regarding their data and also help them to form better big data frameworks. The average annual salary of a big data analyst is around $150,000.
4) Big data developer
A big data developer is responsible for creating efficient codes and monitoring the databases for defects. The salary of a big data developer is around $105,000.
For more awareness about data science, you can explore DASCA
To explore certification programs in your field, chat with our experts, and find the certification that fits your career requirements.
Suggested Read: Data Science vs Data Analytics vs Big Data - Detailed Explanation and Comparison
Subscribe to our Newsletters
Popular Programs
Trending Posts
Big Data Uses Explained with Examples
Last updated on Oct 11 2022
Top DBMS Interview Questions and Answers
Last updated on Feb 27 2024
Data Science Frameworks: A Complete Guide
Last updated on Apr 15 2024
Why Choose Data Science for Career
Last updated on Feb 28 2023
How to Create Data Visualizations in Excel: A Brief Guide
Last updated on Sep 11 2024
Top Selenium Interview Questions and Answers 2024
Last updated on Jan 29 2024
Categories
- Agile Management 54
- AI and Machine Learning 42
- Big Data 53
- Business Management 51
- Cloud Computing 44
- Digital Marketing 56
- Information Security 8
- IT Hardware and Networking 17
- IT Security 103
- IT Service Management 29
- Leadership and Management 1
- Microsoft Program 2
- Other 43
- Programming Language 31
- Project Management 162
- Quality Management 75
- Risk Management 8
- Workplace Skill Building 2
Trending Now
Big Data Uses Explained with Examples
ArticleData Visualization - Top Benefits and Tools
ArticleWhat is Big Data – Types, Trends and Future Explained
ArticleData Analyst Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ArticleData Science vs Data Analytics vs Big Data
ArticleData Visualization Strategy and its Importance
ArticleData Science Guide 2024
ArticleData Science Interview Questions and Answers 2024 (UPDATED)
ArticlePower BI Interview Questions and Answers (UPDATED)
ArticleApache Spark Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ArticleTop Hadoop Interview Questions and Answers 2024 (UPDATED)
ArticleTop DevOps Interview Questions and Answers 2025
ArticleTop Selenium Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ArticleWhy Choose Data Science for Career
ArticleSAS Interview Questions and Answers in 2024
ArticleWhat Is Data Encryption - Types, Algorithms, Techniques & Methods
ArticleHow to Become a Data Scientist - 2024 Guide
ArticleHow to Become a Data Analyst
ArticleBig Data Project Ideas Guide 2024
ArticleHow to Find the Length of List in Python?
ArticleHadoop Framework Guide
ArticleWhat is Hadoop – Understanding the Framework, Modules, Ecosystem, and Uses
ArticleBig Data Certifications in 2024
ArticleHadoop Architecture Guide 101
ArticleData Collection Methods Explained
ArticleData Collection Tools - Top List of Cutting-Edge Tools for Data Excellence
ArticleTop 10 Big Data Analytics Tools 2024
ArticleKafka vs Spark - Comparison Guide
ArticleData Structures Interview Questions
ArticleData Analysis guide
ArticleData Integration Tools and their Types in 2024
ArticleWhat is Data Integration? - A Beginner's Guide
ArticleData Analysis Tools and Trends for 2024
ebookA Brief Guide to Python data structures
ArticleWhat Is Splunk? A Brief Guide To Understanding Splunk For Beginners
ArticleBig Data Engineer Salary and Job Trends in 2024
ArticleWhat is Big Data Analytics? - A Beginner's Guide
ArticleData Analyst vs Data Scientist - Key Differences
ArticleTop DBMS Interview Questions and Answers
ArticleData Science Frameworks: A Complete Guide
ArticleTop Database Interview Questions and Answers
ArticlePower BI Career Opportunities in 2025 - Explore Trending Career Options
ArticleCareer Opportunities in Data Science: Explore Top Career Options in 2024
ArticleCareer Path for Data Analyst Explained
ArticleCareer Paths in Data Analytics: Guide to Advance in Your Career
ArticleA Comprehensive Guide to Thriving Career Paths for Data Scientists
ArticleWhat is Data Visualization? A Comprehensive Guide
ArticleTop 10 Best Data Science Frameworks: For Organizations
ArticleFundamentals of Data Visualization Explained
Article15 Best Python Frameworks for Data Science in 2025
ArticleTop 10 Data Visualization Tips for Clear Communication
ArticleHow to Create Data Visualizations in Excel: A Brief Guide
ebook










