Top 3 Cloud Computing Service Models: SaaS | PaaS | IaaS
-
 By Niharika Chaurasia
By Niharika Chaurasia - Published on Jan 30 2025

Introduction to Cloud Computing Services
In recent times, as more businesses migrate their workloads from on-premises infrastructure to the cloud, cloud computing services and models are gaining tremendous momentum.
Cloud computing has changed the way businesses operate today. With the use of the internet, it has completely transformed the ability to use IT infrastructure, software applications, and platforms.
According to Dell, organisations that invest in big data, cloud, mobility, and security grow their income up to 53% quicker than their competitors. In another report, after migrating to the cloud, 94% of businesses saw an increase in security. 91% stated that the cloud makes meeting government compliance standards easier.
Let us see some of the advantages that cloud computing services offer to businesses:
- Flexibility
- Security
- Cost Savings
- Disaster Recovery
- Increased Collaboration
- Competitive Edge
- Automatic Software Updates
Many companies are eagerly adopting the cloud to get rid of different layers of management. This helps organisations cut costs, save management time, and have a secure and flexible platform to perform IT tasks.
Table of Contents
What Are the Cloud Service Models?
Cloud service Models are a type of service that provides convenient, on-demand network access to a shared pool of configurable computing resources.
These services are basically designed to provide flexible, affordable access to applications and resources that do not require any internal infrastructure or hardware.
Next, let’s see how cloud management services are delivered. So to leverage cloud services, it is necessary for the organisation to decide which type of cloud environment suits their business best. Cloud environments can be public or private, or a mix of both that can be chosen as per the business requirement.
Public cloud services are those that a provider makes available to all customers on the internet. On the other hand, services that a provider does not make available to corporate users or subscribers are referred to as private cloud services.
In a hybrid cloud environment, the services are a combination of both private and public cloud solutions.
What Are the Types of Cloud Service Models?
In general, there are three basic types of cloud service models, which can also be called cloud computing service models. The cloud service models shown in the image below are different from each other with respect to their level of control, management, and flexibility, which enable cloud users to choose a set of services as per their needs.

Now, let’s define each cloud service model and learn the benefits they provide to organization.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
-It’s the most basic and flexible type of cloud service that allows you to rent the hardware and contains the building blocks for cloud and IT.
-IaaS is a computing infrastructure that can be provided and managed instantly over the internet.
-To run applications, it gives complete control (servers, VMs, storage, networks, and operating systems) over the hardware.
-Iaas provides the best level of flexibility and management control of IT resources.
-Many IT departments and developers are using IaaS as common IT resources.
-Iaas is used for storing, recovering, and keeping backups of the data and is also helpful in managing fluctuating storage needs.
-IaaS is often used by companies working with big data; it helps increase their computing power.
Benefits of IaaS
1. Cost savings and Efficient
-Cost effective and efficient mode to deploy, operate, and scale IT infrastructure.
-Only pay for the services that are needed—storage, CPU power, bandwidth, and other resources.
-This makes it easy for the organizations to scale up or down as needed.
2. On-demand access
-On demand access to cloud-hosted computing infrastructure (servers, storage capacity, and networking resources) where customers can provision, configure, and use it in much the same way as they use on-premises hardware.
-The only difference is that a cloud service provider hosts, maintains, and manages the hardware and resources in its own data centres.
3. Flexibility
-Iaas cloud computing model provides flexibility for adding more resources whenever there is increase in demand, without having to upgrade equipment or hire more IT professionals.
Example of IaaS: AWS EC2 or Virtual Machines, Storage, or Networking
Use cases for IaaS

Platform as a Service (PaaS)
- PaaS cloud service model provides a ready-to-use development environment that can be used by developers to write and execute high-quality code to create customised applications.
- Without managing the basic infrastructure, it can quickly create applications. There is no need to install an operating system, a web server, or even system updates; however, the addition of new features and scaling can be done.
- Increases efficiency because it takes care of resource procurement, capacity planning, software maintenance, patching, or any of the undifferentiated efforts needed in running an application.
- The method of developing and deploying applications is made simpler with the help of PaaS, but it is an expensive service compared to IaaS.
- PaaS is accessed by the users through a graphical user interface (GUI), where the development and DevOps teams can interact on all aspects of the application lifecycle, including coding, integration, testing, delivery, deployment, and feedback.
Benefits of PaaS
1. Faster development time
- PaaS cloud service models allow users to build, test, deploy, run, update, and scale applications in less time. You can start coding without building an infrastructure.
- Developers can focus on writing code and creating applications without worrying about time-consuming IT infrastructure activities such as provisioning servers, storing data, and performing backups.
2. Reduced costs
- By using PaaS, IT department can save time on manual deployments and server management.
3. High availability and easy collaboration
- Here high availability means that, even during hardware failure or maintenance of the windows, the application is always available by PaaS service provider.
- PaaS provides a shared software development environment, allowing the development and operations teams to use all of the tools they require from any location through the internet.
4. Enhanced security
- To provide a secure cloud service, PaaS locks down the application.
- PaaS models improve security by increasing business resilience, decreasing downtime, limiting data loss, and allowing for faster data recovery.
Less to maintain
- PaaS offloads infrastructure management, patches, updates, and other related administrative responsibilities to the cloud service provider.
Examples of PaaS: AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Microsoft Windows Azure, and Red Hat OpenShift on IBM Cloud.
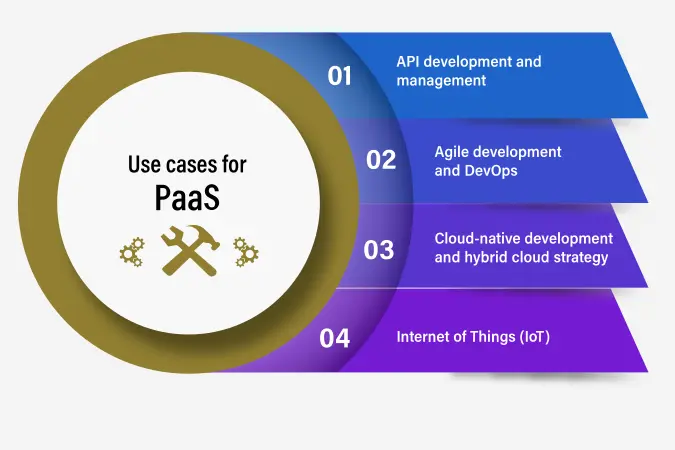
Use cases for PaaS
Software as a Service (SaaS)
- SaaS is also known as cloud application service, which is cloud-hosted, ready-to-use application software.
- By paying a monthly or annual fee, users can use the full programme through a web browser, desktop client, or mobile app.
- SaaS vendors host and manage the application and the entire infrastructure to deliver it, which includes servers, storage, networking, middleware, application software, and data storage.
- Under service level agreement (SLA), the vendor ensures a level of availability, performance, and security.
Benefits of SaaS
1. Productivity at anytime/anywhere
- SaaS cloud service model provides flexibility to work on any device with a browser and an internet connection.
2. Low risk
- SaaS providers offer a free trial period, or low monthly fees that allow customers to try the software to check whether it will meet their requirements. Hence, SaaS offers a low risk of financial losses.
3. Better security
- Provides improved security, since most of the services are hosted on secure servers in data centres with 24/7 monitoring, reducing the chance of hackers gaining access to the server.
- This makes SaaS a better option for storing sensitive information than on a local server or on premises software.
Use cases for SaaS

Examples of SaaS: Microsoft Office 365, Salesforce, Oracle ERP/HCM Cloud, Dropbox, or Gmail.
Conclusion
The Cloud service models are a great solution for all your business needs. While choosing the right service model for your business, it is important to consider the level of flexibility, control, and management that your business requires.
With the growing need for cloud services, cloud computing experts are in high demand. Check out AWS Certification Training Solution Architect if you're seeking for a cloud computing certification to advance your career in this rapidly growing field.
Explore more globally recognised Sprintzeal courses and visit the Sprintzeal blog page for more interesting blogs.
Subscribe to our Newsletters
Popular Programs
Microsoft Azure Administrator Associate AZ-104
Live Virtual Training
- 4.6 (560 + Ratings)
- 46k + Learners
AWS Certified Solution Architect Professional
Live Virtual Training
- 4.2 (300 + Ratings)
- 4k + Learners
AWS Certified DevOps Engineer Certification Training
Live Virtual Training
- 4 (400 + Ratings)
- 49k + Learners
Microsoft Azure Infrastructure Solutions (AZ-305)
Live Virtual Training
- 4.2 (560 + Ratings)
- 30k + Learners
Trending Posts
Jenkins Interview Questions and Answers (UPDATED 2024)
Last updated on Oct 10 2022
Cloud Computing and Fog Computing - Key Differences and Advantages
Last updated on Jun 19 2023
A Step-by-Step Guide to Git
Last updated on Nov 29 2022
IoT Security Challenges and Best Practices-An Overview
Last updated on Mar 20 2023
Azure Vs Aws - Which Technology Is Better
Last updated on Jul 30 2024
What is a Cloud Service - A Beginner's Guide
Last updated on Apr 18 2023
Categories
- Agile Management 54
- AI and Machine Learning 42
- Big Data 53
- Business Management 51
- Cloud Computing 44
- Digital Marketing 56
- Information Security 8
- IT Hardware and Networking 17
- IT Security 103
- IT Service Management 29
- Leadership and Management 1
- Microsoft Program 2
- Other 43
- Programming Language 31
- Project Management 162
- Quality Management 75
- Risk Management 8
- Workplace Skill Building 2
Trending Now
Azure Vs Aws - Which Technology Is Better
ebookThe Impact of Internet of things on Marketing
ebookAWS Lambda - An Essential Guide for Beginners
ebookCareer in Cloud Computing or Cyber Security
ebookImpact of AWS Certification On Cloud Computing Jobs
ebookAmazon Certifications: List of Top AWS certifications in 2024
ebookAWS Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ebookWhat is Cloud Computing? - Fundamentals of Cloud Computing
ebookAmazon Software Development Manager Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ebookAWS Solutions Architect Salary in 2024
ebookAWS Architect Interview Questions - Best of 2024
ebookHow to Become a Cloud Architect - Career, Demand and Certifications
ebookAmazon EC2 - Introduction, Types, Cost and Features
ebookAWS Opsworks - An Overview
ebookAzure Pipeline Creation and Maintenance
ebookCI CD Tools List - Best of 2024
ebookBenefits of Cloud Computing in 2024
ebookTrends Shaping the Future of Cloud Computing
ebookContinuous Deployment Explained
ebookDevOps Career Path – A Comprehensive Guide for 2024
ebookTop Kubernetes Tools in 2024
ArticleJenkins Interview Questions and Answers (UPDATED 2024)
ArticleA Step-by-Step Guide to Git
ArticleScalability in Cloud Computing Explained
ebookIoT Security Challenges and Best Practices-An Overview
ebookHow to Learn Cloud Computing in 2024 - A Brief Guide
ArticleCloud Engineer Roles and Responsibilities: A complete Guide
ebookTypes of Cloud Computing Explained
ArticleCloud Engineer Salary - For Freshers and Experienced in 2024
ArticleEssential Cybersecurity Concepts for beginners
ebookWhat is a Cloud Service - A Beginner's Guide
ebookWhat is Private Cloud? - Definition, Types, Examples, and Best Practices
ebookWhat Is Public Cloud? Everything You Need to Know About it
ArticleTop 15 Private Cloud Providers Dominating 2025
ebookWhat Is a Hybrid Cloud? - A Comprehensive Guide
ebookCloud Computing and Fog Computing - Key Differences and Advantages
ebookAzure Architecture - Detailed Explanation
ArticleMost Popular Applications of Cloud Computing – Some Will Shock You
ArticleTips and Best Practices for Data Breaches in Cloud Computing
ArticleWhat Is Edge Computing? Types, Applications, and the Future
ArticleMust-Have AWS Certifications for Developers in 2025
ArticleSalesforce Customer Relationship Management and its Solutions
ArticleSpotify Cloud: Powering Music Streaming Worldwide
Article