Six Sigma tools for DMAIC Phases
-
 By Sushmith
By Sushmith - Published on Nov 8 2024

What Are DMAIC Tools?
DMAIC is an acronym for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. The DMAIC methodology is a systematic problem-solving methodology widely used in Lean Six Sigma projects to enhance processes and improvements. DMAIC tools help practitioners navigate each phase of this structured approach.
Defining DMAIC Tools
DMAIC tools encompass a diverse set of techniques and methodologies designed to assist in specific phases of the DMAIC process. These tools serve as valuable aids for data collection, analysis, and decision-making, ultimately contributing to the successful execution of Lean Six Sigma projects.

- Define phase tools help in clarifying project goals, scope, and key stakeholders.
- Measure phase tools are used to collect and analyze data to establish the current state of the process.
- Analyze phase tools identify root causes of problems and gaining insights into process behavior.
- Improve phase tools and techniques support the development and implementation of solutions.
- Control phase tools that ensure sustained improvements and maintain process stability.
Let’s dive in and understand the tools used for each of the 5 DMAIC phases and explore how they help in Lean Six Sigma projects.
Table of Contents
- Top 5 tools for each of the DMAIC phases
- DMAIC tools for Define phase
- DMAIC tools for Measure phase
- DMAIC tools for Analyze phase
- DMAIC tools for Improve phase
- DMAIC tools for Control phase
- Selecting the Right DMAIC Tools
- FAQs for DMAIC Tools
- Master DMAIC Tools with Lean Six Sigma Certification Training
- Conclusion
Top 5 tools for each of the DMAIC phases
Effective process improvement relies on choosing the right tools for each step of the DMAIC approach. Every phase demands specific tools to tackle its particular challenges. In this section, we'll explore the top five tools for each phase, explaining how they're used and why they matter for making processes better and ensuring top-notch quality in organizations.
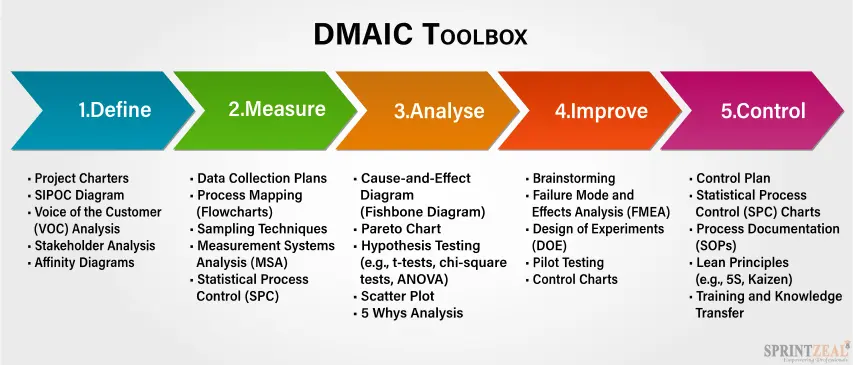
DMAIC tools for Define phase
In the Define phase of the DMAIC methodology, the primary objective is to establish a clear understanding of the problem, project goals, and scope. This phase sets the stage for the entire project, and five key DMAIC tools assist in achieving these critical objectives:
1. Project Charter
What is a Project Charter? A project charter is a foundational document that outlines the purpose, scope, objectives, and key stakeholders of the project. It serves as a roadmap, providing clarity and direction from the very beginning.
How it helps:
- Establishes Purpose: The project charter defines the reason for undertaking the project, ensuring that all team members are aligned with its goals and objectives.
- Defines Scope: It clearly outlines the boundaries of the project, helping the team stay focused on addressing the relevant issues.
- Identifies Stakeholders: The charter lists key stakeholders, ensuring that their needs and expectations are considered throughout the project's lifecycle.
2. SIPOC Diagram
What is a SIPOC Diagram? The SIPOC (Suppliers, Inputs, Process, Outputs, Customers) diagram is a visual representation that provides an overview of the high-level process flow, including its inputs, outputs, and key stakeholders. It is instrumental in identifying areas that require improvement.
How it Helps:
- Process Clarity: SIPOC diagrams offer a clear and concise overview of the process, making it easier to identify its components and interactions.
- Identifies Boundaries: By delineating the process boundaries, the SIPOC helps the team focus on specific process steps critical to the project.
- Stakeholder Inclusion: It highlights the roles of customers and suppliers, ensuring that their perspectives are considered during problem-solving and decision-making.
3. Voice of the Customer (VOC) Analysis
What is VOC Analysis? Understanding the customer's needs and expectations is paramount. VOC analysis tools, such as surveys, interviews, and direct feedback collection, help gather customer insights and translate them into actionable project goals.
How it Helps:
- Customer-Centric Approach: VOC analysis ensures that project objectives are closely aligned with what customers value most, fostering customer satisfaction and loyalty.
- Data-Driven Insights: It provides invaluable data and insights directly from customers, guiding project decisions based on actual customer preferences.
- Prioritization: VOC analysis helps prioritize project objectives based on the significance of specific customer needs and their potential impact on satisfaction.
4. Affinity Diagram
What is an Affinity Diagram? An affinity diagram is a tool used to organize and group large amounts of unstructured information or ideas into meaningful categories. It is particularly useful when dealing with complex or unclear problem statements.
How it Helps:
- Idea Organization: Affinity diagrams help in structuring and categorizing ideas or data gathered during the project's initial stages.
- Pattern Recognition: It allows teams to identify patterns and relationships among various pieces of information, leading to deeper insights.
- Enhanced Problem Definition: Organizing information coherently, contributes to refining the problem statement and project objectives.
5. Stakeholder Analysis
What is Stakeholder Analysis? Stakeholder analysis is a systematic process of identifying and assessing the interests, influence, and potential impact of individuals or groups that have an interest in the project.
How it Helps:
- Prioritization of Stakeholders: Stakeholder analysis helps in determining which stakeholders have the most significant influence on the project's success.
- Communication Strategy: It informs the development of tailored communication plans and engagement strategies for different stakeholder groups.
- Risk Mitigation: By understanding stakeholder interests and potential concerns, the team can proactively address issues that may arise during the project.
In the Define phase, these five DMAIC tools play a pivotal role in laying a solid foundation for your Lean Six Sigma project. They facilitate the process of defining the problem, project scope, and stakeholder expectations, all of which are essential for a successful project journey.
DMAIC tools for Measure phase
In the Measure phase of the DMAIC methodology, the primary focus is on collecting and analyzing data to establish the current state of the process. The following DMAIC tools are instrumental in achieving these objectives:
1. Data Collection Plan
What is a Data Collection Plan? A data collection plan is a structured document that outlines what data needs to be collected, how it will be collected when it will be collected, and who will be responsible for data gathering. It ensures that data is collected systematically and accurately.
How it Helps:
- Systematic Data Gathering: Provides a clear plan for collecting relevant data points in an organized manner.
- Reduces Bias: Minimizes the risk of bias in data collection by specifying methods and procedures.
- Efficient Resource Allocation: Helps allocate resources efficiently for data collection activities.
2. Process Mapping
What is Process Mapping? Process mapping tools like flowcharts and value stream maps provide a visual representation of the process. They help in understanding the sequence of steps, inputs, and outputs in the process.
How it Helps:
- Visual Clarity: Offers a clear visual representation of the process, making it easier to identify bottlenecks and inefficiencies.
- Identifies Handoffs: Highlights points where work is handed off between individuals or departments, which can be sources of delays.
- Root Cause Analysis: Facilitates the identification of areas within the process that may need improvement.
3. Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA)
What is Measurement Systems Analysis (MSA)? MSA tools assess the accuracy, precision, and reliability of measurement systems to ensure that collected data is trustworthy. Common MSA techniques include Gage R&R (Repeatability and Reproducibility) studies.
How it Helps:
- Data Reliability: Ensures that measurement instruments and methods are reliable, reducing the risk of incorrect conclusions.
- Identifies Measurement Error: Helps identify and quantify sources of measurement error, allowing for data correction.
- Improves Decision-Making: Reliable measurements lead to better-informed decisions.
4. Histograms and Frequency Plots
What are Histograms and Frequency Plots? Histograms and frequency plots are graphical tools used to display the distribution of data. Histograms provide a visual representation of data distribution, while frequency plots show how data points are distributed across different categories or bins.
How they Help:
- Data Distribution Visualization: Provides a clear picture of how data is distributed, whether it's normally distributed or skewed.
- Identifies Patterns: Helps identify patterns or outliers in the data, which may indicate process variations.
- Basis for Analysis: Serves as the foundation for further statistical analysis.
5. Process Capability Analysis
What is Process Capability Analysis? Process capability analysis assesses the ability of a process to consistently produce products or services that meet customer specifications. Common metrics used in process capability analysis include Cp, Cpk, Pp, and Ppk.
How it Helps:
- Quality Assessment: Determines whether a process is capable of producing products or services within customer-defined limits.
- Focuses Improvement Efforts: Identifies areas where process capability falls short, guiding improvement efforts.
Predictive Insights: Helps predict the likelihood of producing defects or non-conforming products.
DMAIC tools for Analyze phase
The Analyze phase of the DMAIC methodology focuses on identifying the root causes of problems and gaining insights into process behavior. To achieve these objectives, various DMAIC tools are employed:
1. Cause-and-Effect Diagram (Fishbone Diagram)
What is a Cause-and-Effect Diagram? Also known as a Fishbone or Ishikawa diagram, this tool helps visualize potential causes of a problem. It resembles a fishbone, with the problem statement at the "head" and branches representing different categories of potential causes.
How it Helps:
- Root Cause Identification: Facilitates a structured approach to identifying root causes by breaking down potential contributors.
- Team Collaboration: Encourages team collaboration and brainstorming to explore various causes.
- Visual Representation: Provides a clear and visual overview of the problem's causes and their relationships.
2. Pareto Chart
What is a Pareto Chart? A Pareto chart is a bar chart that prioritizes issues or causes by showing which factors contribute the most to a problem. It follows the Pareto principle, suggesting that a small number of causes (the "vital few") often account for the majority of the problems.
How it Helps:
- Prioritization: Helps prioritize improvement efforts by focusing on the most significant contributors to the problem.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Provides a data-driven basis for determining where resources should be allocated.
- Visual Clarity: Offers a clear visual representation of the most critical issues.
3. Hypothesis Testing
What is Hypothesis Testing? Hypothesis testing involves using statistical methods to analyze data and test hypotheses about potential root causes. Common tests include t-tests, chi-square tests, and ANOVA (Analysis of Variance).
How it Helps:
- Statistical Validation: Validates whether a potential cause is statistically significant in contributing to the problem.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Provides a rigorous approach to making decisions based on data.
- Evidence-Based Insights: Offers insights into which factors are likely causing the observed issues.
4. Scatter Plot
What is a Scatter Plot? A scatter plot displays data points on a two-dimensional graph, with one variable on the x-axis and another on the y-axis. It is used to explore relationships and correlations between variables.
How it Helps:
- Visualizing Relationships: Helps visualize the relationship between two variables, indicating whether they are positively, negatively, or not correlated.
- Identification of Patterns: Can reveal patterns, trends, or outliers in the data.
- Data-Driven Insights: Provides a basis for making informed decisions about potential causes.
5. Five Whys Analysis
What is 5 Whys Analysis? The 5 Whys technique involves repeatedly asking "Why?" to dig deeper into the root cause of a problem. By asking "Why?" five times (or more), it aims to uncover the underlying issues.
How it Helps:
- Systematic Inquiry: Encourages a systematic and structured approach to uncovering root causes.
- Deep Understanding: Helps reach the core issues rather than addressing surface-level symptoms.
- Simplicity: A straightforward yet effective technique for root cause analysis.
DMAIC tools for Improve phase
In the Improve phase of the DMAIC methodology, the focus shifts to developing and implementing solutions to address the root causes identified during the Analyze phase. The following DMAIC tools and techniques are instrumental in driving process improvement:
1. Brainstorming
What is Brainstorming? Brainstorming is a creative problem-solving technique that involves generating a wide range of ideas and potential solutions. Team members collaborate to explore innovative ways to address identified issues.
How it Helps:
- Idea Generation: Encourages the generation of diverse ideas and solutions from team members.
- Promotes Teamwork: Fosters collaboration and participation, allowing for a variety of perspectives.
- Divergent Thinking: Supports thinking "outside the box" to identify novel solutions.
2. Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA)
What is FMEA? FMEA is a systematic approach to evaluating potential failure modes within a process and their potential impact. It assigns scores for Severity, Occurrence, and Detection to prioritize which failure modes to address first.
How it Helps:
- Risk Prioritization: Identifies high-priority failure modes that pose the greatest risk to the process.
- Structured Approach: Provides a structured framework for analyzing and addressing potential failures.
- Focus on Prevention: Helps teams proactively address issues before they occur.
3. Design of Experiments (DOE)
What is the Design of Experiments (DOE)? DOE is a statistical technique used to systematically vary and analyze multiple factors simultaneously to optimize a process. It helps identify the ideal combination of factors that produce the desired outcomes.
How it Helps:
- Optimization: Aids in finding the most efficient and effective combination of process variables.
- Reduces Variation: Helps reduce process variability by identifying and controlling influential factors.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Provides empirical evidence for process improvements.
4. Pilot Testing
What is Pilot Testing? Pilot testing involves implementing proposed process improvements on a smaller scale before full-scale implementation. It allows for testing and refinement of solutions while minimizing risk.
How it Helps:
- Risk Mitigation: Reduces the risk of implementing changes that may have unforeseen negative consequences.
- Refinement: Provides an opportunity to fine-tune solutions based on real-world testing.
- Validation: Ensures that proposed improvements work effectively in practice.
5. Control Charts
What are Control Charts? Control charts are graphical tools used to monitor and visualize process performance over time. They help identify trends, shifts, or abnormal variations in the process.
How they Help:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Allow for continuous monitoring of process performance.
- Early Detection: Highlight deviations from the desired process state, enabling timely corrective actions.
- Process Stability: Help ensure that improvements are sustained over the long term.
DMAIC tools for Control phase
1. Control Charts
What are Control Charts? Control charts are graphical tools used to monitor and visualize process performance over time. They help identify trends, shifts, or abnormal variations in the process.
How they Help:
- Real-Time Monitoring: Allow for continuous monitoring of process performance.
- Early Detection: Highlight deviations from the desired process state, enabling timely corrective actions.
- Process Stability: Help ensure that improvements are sustained over the long term.
2. Statistical Process Control (SPC) Charts
What are SPC Charts? SPC charts, including control charts and run charts, are used to monitor process stability and identify variations. They provide a visual representation of data over time.
How they Help:
- Continuous Monitoring: Enable real-time monitoring of process variation and performance.
- Early Detection: Alert teams to potential issues or deviations before they impact product or service quality.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Support decisions based on factual data.
3. 5S Methodology
What is the 5S Methodology? The 5S methodology focuses on organizing and maintaining a clean, efficient, and safe work environment. It comprises five principles: Sort, Set in order, Shine, Standardize, and Sustain.
How it Helps:
- Efficiency: Reduces waste, enhances organization, and improves efficiency.
- Safety: Promotes a safe and clutter-free workplace.
- Sustainability: Encourages a culture of cleanliness and orderliness.
4. Poka-Yoke (Mistake-Proofing)
What is Poka-Yoke? Poka-Yoke refers to error-proofing or mistake-proofing techniques designed to prevent errors and defects during the production or operation of a process. These can include simple mechanisms or processes that prevent mistakes.
How it Helps:
- Error Prevention: Eliminates the possibility of errors or defects at their source.
- Quality Improvement: Ensures that products or services are produced correctly the first time.
- Cost Reduction: Reduces the need for rework or corrections.
5. Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)
What are Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs)? SOPs are documented step-by-step instructions that detail how specific tasks or processes should be performed. They provide a consistent and standardized approach to tasks.
How they Help:
- Consistency: Ensure that tasks are performed consistently and correctly.
- Training: Aid in the training of new employees by providing clear instructions.
- Compliance: Support compliance with regulatory requirements and quality standards.
Selecting the Right DMAIC Tools
Selecting the right DMAIC tools is crucial for the success of your Lean Six Sigma project. The choice of tools should be driven by the specific objectives of each phase and the nature of the problem you're addressing. Here's a guide to help you select the most appropriate tools for your project:
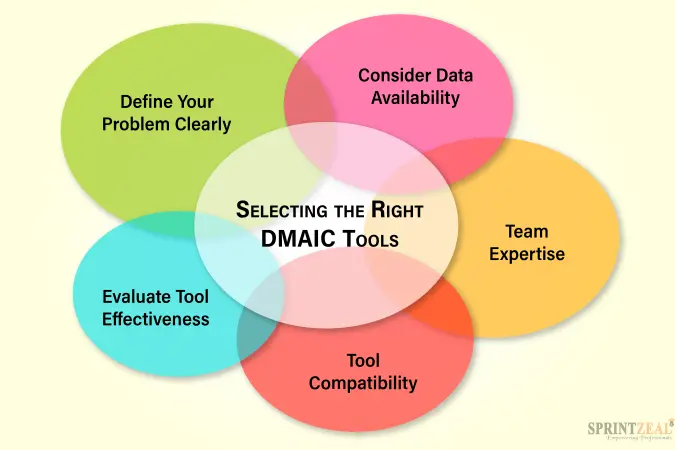
- Define Your Problem Clearly
Before choosing DMAIC tools, ensure you have a clear and concise understanding of the problem you're trying to solve. Define the problem statement, its scope, and the goals of your project. This clarity will guide your tool selection.
- Consider the DMAIC Phase
Different phases of the DMAIC process require different tools. For example:
1. In the Define phase, tools like Project Charters and SIPOC diagrams help scope and understand the problem.
2. In the Measure phase, tools like Data Collection Plans and Process Mapping are valuable for data collection and process assessment.
3. In the analysis phase, tools like Cause-and-Effect diagrams and Hypothesis Testing help identify root causes.
4. In the Improve phase, tools like Brainstorming and Design of Experiments support solution development.
5. In the Control phase, Control Charts and Standard Operating Procedures help sustain improvements.
- Consider Data Availability
The availability of data can influence your tool selection. If data is limited, focus on tools that can work with the available data or consider data collection methods for missing information.
- Team Expertise
Assess the expertise of your project team. Some tools may require specialized knowledge or training. Ensure that your team is comfortable using the selected tools or invest in training if needed.
- Tool Compatibility
Ensure that the chosen DMAIC tools are compatible with your organization's systems and processes. This includes considering software compatibility, data integration, and overall alignment with existing practices.
- Evaluate Tool Effectiveness
Regularly evaluate the effectiveness of the tools you're using. If a tool is not producing the desired results or insights, be open to adjusting your approach and considering alternative tools.
- Seek Guidance
Don't hesitate to seek guidance from experienced Lean Six Sigma practitioners, mentors, or consultants. They can provide valuable insights into which tools are best suited to your specific project and organizational context.
- Documentation
Document your tool selection process and rationale. This documentation will not only help you make informed decisions but also serve as a reference for future projects.
Remember that the effectiveness of DMAIC tools relies on their appropriate application within the context of your project. Selecting the right tools and using them effectively is a key factor in achieving successful outcomes and process improvements.
FAQs for DMAIC Tools
Best DMAIC Tools for the Analyze Phase?
Some of the best DMAIC tools commonly used in the Analyze phase include:
- Cause-and-Effect Diagram (Fishbone Diagram)
- Pareto Chart
- Hypothesis Testing
- Scatter Plot
- 5 Whys Analysis
What Tools Are Most Commonly Used in DMAIC?
DMAIC involves a wide range of tools, and the choice of tools depends on the specific phase of the DMAIC process and the nature of the problem being addressed. However, some commonly used tools across the DMAIC phases include:
- Define Phase: Project Charters, SIPOC diagrams.
- Measure Phase: Data Collection Plans, Process Mapping.
- Analyze Phase: Cause-and-Effect Diagrams, Pareto Charts, Hypothesis Testing.
- Improve Phase: Brainstorming, Design of Experiments (DOE).
- Control Phase: Control Charts, Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs).
What Is the Purpose of DMAIC Tools?
The purpose of DMAIC tools is to provide a structured and systematic approach to problem-solving and process improvement. These tools help organizations:
- Identify and define problems or challenges.
- Measure and analyze data to understand the current state of processes.
- Analyze root causes of problems.
- Develop and implement effective solutions.
- Maintain and control improved processes to ensure sustainability and consistency.
DMAIC tools promote data-driven decision-making and continuous improvement within an organization.
Is DMAIC a Problem-Solving Tool?
DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control) is not a single problem-solving tool but a comprehensive problem-solving methodology used in Lean Six Sigma. It incorporates a wide range of tools and techniques at each phase to address specific aspects of process improvement and problem-solving. DMAIC provides a structured framework for identifying, analyzing, and resolving problems to enhance process performance and quality.
Master DMAIC Tools with Lean Six Sigma Certification Training
Improving your expertise in DMAIC tools and Lean Six Sigma methods is a valuable journey that can greatly benefit your career and your company's achievements. Lean Six Sigma Certification Training is the path to gaining this expertise in a structured and hands-on way.
Sprintzeal's Lean Six Sigma Certification Training is your gateway to achieving expertise in a structured and practical manner.
Our comprehensive training programs provide an in-depth understanding of DMAIC tools, principles, and methodologies. You'll gain hands-on experience, working on real projects that empower you to confidently apply DMAIC tools in your workplace. With a strong emphasis on problem-solving and critical-thinking skills, our training equips you to identify and address process issues efficiently.
Quality optimization and career advancement await you. Sprintzeal's Lean Six Sigma Certification opens doors to new opportunities, positioning you as a valued professional in quality management, process improvement, and leadership roles. Don't miss your chance to become a Lean Six Sigma expert—visit our Lean Six Sigma Certification Training page to embark on your DMAIC tools mastery journey with Sprintzeal today.
Conclusion
In this guide, we've explored DMAIC tools, pivotal in Lean Six Sigma methodology. From Define to Control, these tools empower organizations to enhance efficiency and deliver higher-quality products and services. Applying the right tool at the right time is the key to identifying root causes and achieving sustained improvements. Now, let's take your understanding of DMAIC tools further by considering Lean Six Sigma Certification Training.
In conclusion, DMAIC tools are vital for process improvement and quality optimization across diverse industries. Their universal applicability makes them a critical asset for organizations striving to reduce costs and enhance product and service delivery.
Consider taking your knowledge of DMAIC tools to the next level through Lean Six Sigma Certification Training. Sprintzeal offers comprehensive training programs designed to equip you with the expertise needed to excel in process improvement. Our experienced instructors, practical projects, and respected certifications validate your proficiency in DMAIC tools and Lean Six Sigma methodologies.
Visit our home page Sprintzeal.com to explore your options and start your path to excellence in process improvement and quality optimization. Your DMAIC tools mastery journey begins here.
Subscribe to our Newsletters
Popular Programs
Trending Posts
How to Effectively Implement a Robust Quality Management System?
Last updated on Aug 26 2024
Learn about Statistical Process Control (SPC) and its top applications
Last updated on Mar 21 2023
Six Sigma Certifications - Reasons Why you Should Get Them
Last updated on Aug 18 2022
Quality Management Interview Questions 2024
Last updated on Sep 21 2022
Service Delivery Manager Interview Questions and Answers (With Examples)
Last updated on Oct 31 2024
Introduction to Lean Manufacturing- Definitions, Framework, and More
Last updated on Nov 15 2023
Categories
- Agile Management 55
- AI and Machine Learning 44
- Big Data 53
- Business Management 52
- Cloud Computing 44
- Digital Marketing 56
- Information Security 8
- IT Hardware and Networking 17
- IT Security 103
- IT Service Management 29
- Leadership and Management 1
- Microsoft Program 2
- Other 45
- Programming Language 31
- Project Management 162
- Quality Management 75
- Risk Management 8
- Workplace Skill Building 2
Trending Now
Top Career benefits of Lean Six Sigma Green Belt
ArticleLean methodology, Six Sigma methodology and Lean Six Sigma Explained
ArticleSix Sigma Black Belt Certification – Value and Career Benefits in 2024
ArticlePareto Chart in Six Sigma - Explained
ArticleQuality Management Interview Questions 2024
ArticleSix Sigma Certification Guide - A Professional's Guide
ArticleSix Sigma Yellow Belt Certification - Six Sigma for Beginners
ArticleQuality Control Explained – Six Sigma
ArticleTotal Quality Management - A Complete Guide for Beginners
ArticleQuality Assurance in Six Sigma Explained
ArticleQuality Assurance vs Quality Control
ArticleSix Sigma Certification – Everything you Need to Know About Getting Certified
ArticleLean Six Sigma on Resume for Rewarding Career Benefits
ArticleQuality Manager Interview Questions and Answers for 2025
ebookService Delivery Manager Interview Questions and Answers (With Examples)
ArticleSix Sigma Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ArticleHow to become a Quality Analyst
ArticleA Supply Chain Management Guide to Mastering Logistics End to End
ArticleSenior Quality Manager Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ArticleTop 30 Quality Analyst Interview Questions and Answers 2025
ArticleFinancial Analyst Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ArticleRisk Manager Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ArticleCompliance Manager Interview Questions and Answers 2024
ArticleOperation Manager Interview Questions and Answers
Article5 Lean Continuous Improvement Principles to Supercharge Your Operations
ArticleHow to Become a Quality Manager - Career, Job Scope and Certifications
ArticleEssential Components of a Quality Management System
ArticleSix Sigma Certifications - Reasons Why you Should Get Them
ArticleTop Qualities of a Good Manager and a Leader
ArticleLearn about Statistical Process Control (SPC) and its top applications
ArticleCost of Poor Quality - A Detailed Guide
ArticleImplementing 5S Methodology for Better Work Efficiency
ArticleWhat Is Lean Management?
ArticleBest Six Sigma Books in 2024
ArticleLeadership vs Management - The Ultimate Guide
ArticleQuality Assurance Plan - Six Steps To Quality Assurance Plan
ArticleOperational Planning Creation, Key Elements and its Benefits
ArticleA Complete Guide to Product Life Cycle Stages 2025
ArticleWhat Is Lean Manufacturing?- An Overview
ArticleThe Lean Continuous Improvement Model: A Comprehensive Guide
ArticleDMAIC vs. DMADV: Key Differences and Choosing the Right Six Sigma Methodology
ArticleA Deep Dive into the Power of Lean Continuous Improvement Process
ArticleLean Continuous Improvement Methods for Business Excellence
ArticleIntroduction to Lean Manufacturing- Definitions, Framework, and More
ArticleUnderstanding the Key Principles of Lean Manufacturing
ArticleSecret to Unlock Organizational Excellence: Stages of Continuous Improvement
ArticleLean Continuous Improvement: A Detailed Guide to Mastering Organizational Quality
ArticleLean Waste Management: The Ultimate Guide 2023
ArticleA Deep Dive into Lean Continuous Improvement Tools
Article8 Wastes of Lean - Strategies for Identification and Elimination
ArticleThe Ultimate Guide to Lean Manufacturing
ArticleUnderstanding Lean Manufacturing's Pros and Cons
ArticleLean Waste Reduction Strategies: Boost Efficiency and Cut Costs
ArticleTop 10 Lean Manufacturing Tools for Optimal Productivity
ArticleBeyond the Basics: Benefits of Lean Continuous Improvement
ArticleWhat are Quality Standards? | A Guide to ISO Standards
Article7 Important Types of Quality Management System
ArticleA Comprehensive Guide to Quality Management Systems
ArticleISO 9001 Standard: Benefits and Certification
ArticleBenefits of QMS Certification for Your Business
ArticleStep-by-Step Implementation Guide to ISO 9001
ArticleThe Ultimate Guide to ISO 9001: Boosting Quality and Certification Success
ArticleQuality Management System – QSM Approaches and Methodologies
ArticleHow to Effectively Implement a Robust Quality Management System?
ArticleExplaining QMS Documentation Structure: Benefits and Best Practices
ArticleWho Needs ISO 9001 Certification and Why?
ArticleKey Elements of ISO 9001:2015 Quality Management System
ArticleOvercoming Common Challenges in ISO 9001 Certification: Tips and Best Practices
ArticleBest Quality Management Tools
ArticleTotal Quality Management (TQM) vs. Six Sigma
ArticleQuality Manager Salary: What Freshers & Experts Earn in 2025
ArticleCertified Scrum Product Owner: Job Roles And Responsibilities
ArticleTips for Continuous Integration Testing: Streamlining QA
Article10 Quality Management Strategies Adopted by Top Managers
Article


















